The EOF architecture model
Services within the EOF Ecosystem are grouped into two categories: Foundation Services, which ensure the ecosystem’s core functionality, and Value-Creation Services, which deliver additional capabilities and value.
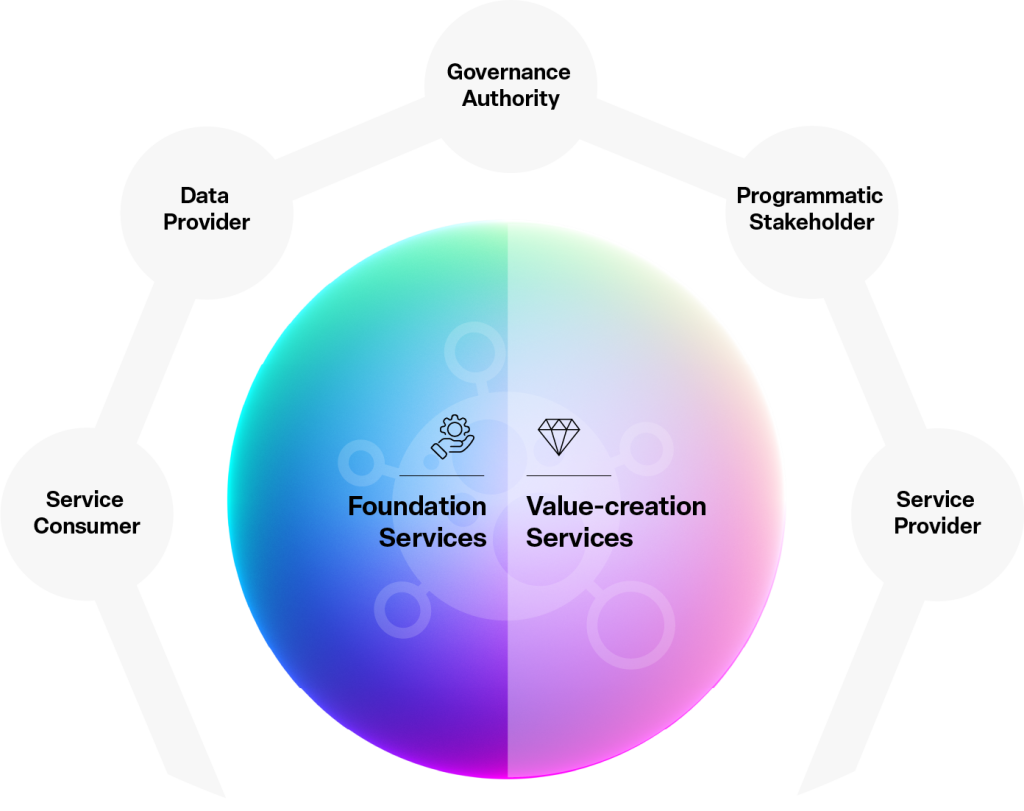
Foundation Services
These services provide the foundation capabilities, encompassing all the activities necessary to enable the deployment and operations of the value-creation services.
They support the interplay of participants in the EOF ecosystem according to the EOF quality and security principles.
ESA supports the implementation and maintenance of the EOF Foundation services through industrial procurements which include the provision of infrastructure resources.
Value-creation services
The value-creation services are industrial services relying on the Foundation Services for an efficient deployment and operations, offering additional capacities, capabilities and data or information.
A particular case of value-creation services are industrial services enabling ESA to execute its mandated role in the context of Earth Observation and Climate actions (e.g. Copernicus Space Component or EO Science missions and data management, DestinE activities entrusted to ESA, DTE Programme activities).
Value-creation services delivered to ESA are often implemented through industrial procurements, ensuring the required levels of performance, quality, and commitment in line with the specific ESA programme needs.
| Feature | EOF Ecosystem |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Trusted, sovereign data exchange, enabling services deployment, delivery and transactions between services |
| Architecture | European Decentralised |
| Scope | ESA EO and Climate activities (initial scope, compatible with any initiative managing space-observations derived datasets) |
| Governance | ESA lead, but as open as possible through co-design and collaboration, ready to contribute formally to European Data Spaces. |
| Data Ownership | Data Owners and Data Licensors retain ownership and control. |
| Trust mechanism | Full adoption of European Regulations, trust is embedded in the architecture and quality framework to monitor, enforce rules. |
EOF Ecosystem Participants
The EOF ecosystem involves key roles each with defined responsibilities to support operations and governance management.
Governance Authority
The entity in charge of defining the governance framework applicable to the EOF ecosystem.
- ESA leads the EOF Ecosystem governance, through co-design and collaboration, and holds ultimate responsibility for decision-making within the EOF ecosystem.
- ESA implements the necessary means to monitor and enforce the compliance to the governance rules.
Data Provider
A Data Provider is a Service Provider that makes data technically available in the EOF ecosystem, typically to be transmitted to a service consumer on behalf of a Data Owner.
Programmatic Stakeholder
Entity(ies) acting as European programme coordinator(s), programmatic governance authority(ies) or shared programmatic governance authority(ies) and funding authority(ies) for a European Programme.
Service consumer
An individual that has performed a Participant Onboarding process in the EOF ecosystem and consumes a set of resources according to a defined role.
Service consumers are individual or legal entities that have the legal right to access and use data of a Data Owner as specified by relevant access and usage policy.
Service Provider
An entity providing services to the EOF ecosystem. Service Providers have undergone a Participant Onboarding process and a service Onboarding process as per EOF specification.
EOF Ecosystem Resources
A Resource is defined and identified as an abstract concept covering what can be provided and/or consumed in the frame of EOF ecosystem via a dedicated EOF service.
Data Sharing Units
Data units—including Earth system models and space observations derived datasets—bundled with metadata and licensing terms, supporting diverse applications and made accessible through web services and APIs, with access controlled by token-based policies.
Applications
Software packages, libraries or algorithms that perform a specific function and that can be installed within an infrastructure to exchange or process data on behalf of EOF Participants.
Service resources
Specific set of capabilities, features, and operations that a service provides to its users via dedicated interfaces, enabling them to derive information from EOF data sharing units.
EOF ecosystem Operational Scenarios
EOF operational scenarios define the core processes that guide the functioning of the ecosystem. These are organized into three main categories to reflect the dynamic nature of the EOF service delivery process.
Interfaces Management
Defines how Participants, Services, and Data Sharing Units join, interact with, and exit the EOF ecosystem, ensuring smooth service integration and ecosystem evolution.
Resources Management
Focuses on the operational workflows for delivering services and managing Resources across the EOF ecosystem.
Value Generation
Details the enforcement of rules, policies, and compliance mechanisms that govern activity within EOF.
The EOF architecture aims at eco-sustainability
Enable the creation of services that can
positively impact the environment